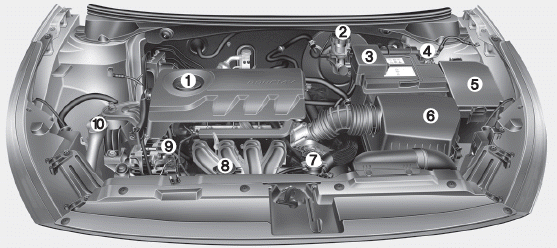
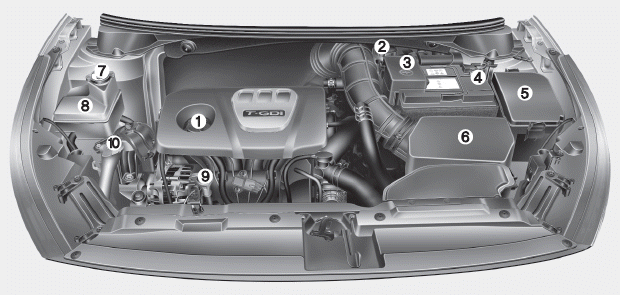
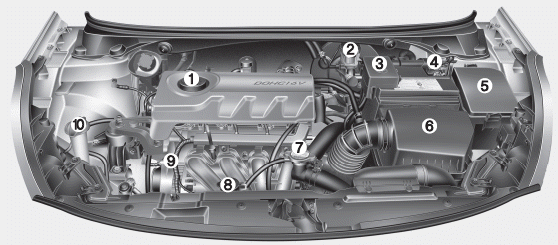
Unlock the Secrets of the Kia Ceed Engine with This Diagram
The Kia Ceed, a popular choice for its reliability, fuel efficiency, and modern design, has won the hearts of drivers worldwide. But beneath its sleek exterior lies a complex machine: the engine. Understanding the engine is crucial for maintaining your Ceed, troubleshooting problems, and even optimizing its performance. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the Kia Ceed engine, utilizing a helpful diagram to demystify its inner workings. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of your car’s powerhouse and how to keep it running smoothly.
Understanding the Kia Ceed Engine: Why It Matters
Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a casual driver, knowing about your car’s engine is beneficial. It helps with:
- Preventive Maintenance: Understanding the components allows you to identify potential issues before they become major problems.
- Troubleshooting: If your car is experiencing issues, knowing the engine’s layout can help you pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Performance Optimization: Understanding how different parts work together can help you optimize your driving habits and potentially improve fuel efficiency.
- Informed Repairs: When visiting a mechanic, a basic understanding of your engine empowers you to ask informed questions and understand the necessary repairs.
The Kia Ceed Engine Diagram: A Visual Guide
(Insert a clear, high-quality diagram of a Kia Ceed engine here. The diagram should be labelled with key components. If you cannot create a diagram, you can describe the key components and their locations. For example:)
While we cannot provide a visual diagram directly, let’s break down the key components and their approximate locations within a typical Kia Ceed engine:
- Cylinder Block: The main body of the engine, housing the cylinders where combustion occurs. Located at the base of the engine.
- Cylinders: Chambers within the cylinder block where the pistons move up and down.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, driven by the expanding gases from combustion.
- Crankshaft: Converts the pistons’ linear motion into rotational motion, which drives the wheels. Located at the bottom of the engine, connected to the pistons via connecting rods.
- Connecting Rods: Connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Cylinder Head: Sits on top of the cylinder block, housing the valves and spark plugs.
- Valves (Intake & Exhaust): Control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and exhaust gases out. Located within the cylinder head.
- Camshaft: Opens and closes the valves, timed to the crankshaft’s rotation. Located within the cylinder head.
- Spark Plugs: Ignite the air-fuel mixture within the cylinders. Located within the cylinder head, screwed into the top of the cylinder.
- Fuel Injectors: Inject fuel into the cylinders (or intake manifold, depending on the engine design).
- Intake Manifold: Distributes air and fuel mixture to the cylinders.
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the cylinders.
- Oil Pan: Holds the engine oil, located at the bottom of the engine.
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil throughout the engine to lubricate moving parts.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant to regulate engine temperature.
- Timing Belt or Chain: Connects the crankshaft to the camshaft, ensuring proper timing of the valves.
- Alternator: Generates electricity to power the car’s electrical systems and charge the battery.
- Starter Motor: Initiates the engine’s combustion process.
(Note: This list is a general overview. Specific engine configurations within the Kia Ceed range may vary slightly.)
Key Components and Their Functions
Let’s delve deeper into some of the most critical components and their roles:
- The Crankshaft: The heart of the engine. It converts the reciprocating (up-and-down) motion of the pistons into the rotational motion that drives the wheels.
- The Camshaft: This is responsible for opening and closing the intake and exhaust valves. Its timing is crucial for efficient engine performance.
- The Fuel System: This system, including the fuel injectors and fuel pump, delivers the correct amount of fuel to the engine. It’s vital for combustion.
- The Cooling System: The cooling system, including the radiator and water pump, keeps the engine from overheating. Overheating can cause significant damage.
- The Ignition System: This system, including the spark plugs and ignition coils, provides the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture.
Common Engine Issues and How to Spot Them
Being aware of potential engine problems can help you take preventative measures. Here are some common issues:
- Loss of Power: Can indicate a problem with the fuel system, ignition system, or compression.
- Rough Idling: Can be caused by issues with spark plugs, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks.
- Engine Knocking or Pinging: Often caused by improper fuel octane or carbon buildup.
- Excessive Oil Consumption: Can indicate worn piston rings or valve seals.
- Overheating: Can be caused by a coolant leak, a faulty water pump, or a malfunctioning thermostat.
- Check Engine Light: A warning that something is wrong. Get the code read by a mechanic.
Maintenance Tips for a Healthy Kia Ceed Engine
Regular maintenance is key to a long-lasting engine:
- Follow the Recommended Service Schedule: Refer to your owner’s manual for the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals.
- Change Oil and Filter Regularly: This is crucial for lubricating the engine and removing contaminants.
- Check and Maintain Coolant Levels: Ensure your engine stays within its optimal operating temperature range.
- Inspect and Replace Spark Plugs: Spark plugs should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check and Replace Air Filter: A clean air filter improves engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Monitor Fluid Levels: Regularly check the oil, coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid levels.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Kia Ceed Ownership
Understanding the Kia Ceed engine, even at a basic level, empowers you to be a more informed and responsible car owner. By utilizing the provided diagram (or the descriptive breakdown if a diagram is unavailable) and understanding the functions of key components, you can proactively maintain your vehicle, troubleshoot potential issues, and potentially extend its lifespan. This knowledge allows you to take better care of your investment and enjoy the reliable performance your Kia Ceed offers for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most common cause of engine failure in a Kia Ceed?
While there’s no single “most common” cause, neglecting regular oil changes and allowing the engine to overheat are significant contributors to engine problems.
2. How often should I change the oil in my Kia Ceed?
Refer to your owner’s manual. Generally, most modern Kia Ceeds recommend oil changes every 7,500 to 10,000 miles, or annually, whichever comes first. However, driving conditions can affect the frequency.
3. What type of fuel should I use in my Kia Ceed?
The recommended fuel type is usually specified in your owner’s manual. Using the correct octane fuel is essential for optimal engine performance and longevity.
4. What does the “check engine” light mean?
The “check engine” light indicates that the engine’s computer has detected a problem. It could be a minor issue or something more serious. It’s crucial to get the code read by a mechanic to diagnose the problem.
5. Can I perform engine maintenance myself?
Some basic maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and spark plug replacements, are often manageable for DIY enthusiasts. However, more complex repairs should be left to qualified mechanics. Always consult your owner’s manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.