The Ultimate Guide to BPC-157: Half-Life, Dosage, and Administration
BPC-157, short for Body Protection Compound-157, has garnered significant attention in the health and wellness community. This synthetic peptide, derived from human gastric juice, is lauded for its potential regenerative and healing properties. Understanding its half-life and proper dosage is crucial for anyone considering its use. This comprehensive guide provides a clear and informed overview of BPC-157, addressing key considerations for safe and effective administration.
What is BPC-157? A Primer
Before diving into the specifics of half-life and dosage, it’s essential to understand what BPC-157 is and what it is purported to do. BPC-157 is a peptide consisting of 15 amino acids. It’s believed to promote healing and recovery by:
- Accelerating Tissue Repair: Potentially aiding in the healing of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and other tissues.
- Reducing Inflammation: Showing promise in reducing inflammatory responses throughout the body.
- Protecting the Gut: Possibly supporting gut health and potentially healing the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Promoting Angiogenesis: Encouraging the formation of new blood vessels, which is crucial for healing.
It’s important to remember that while research is ongoing, the full extent of BPC-157’s effects and its long-term safety are still being investigated.
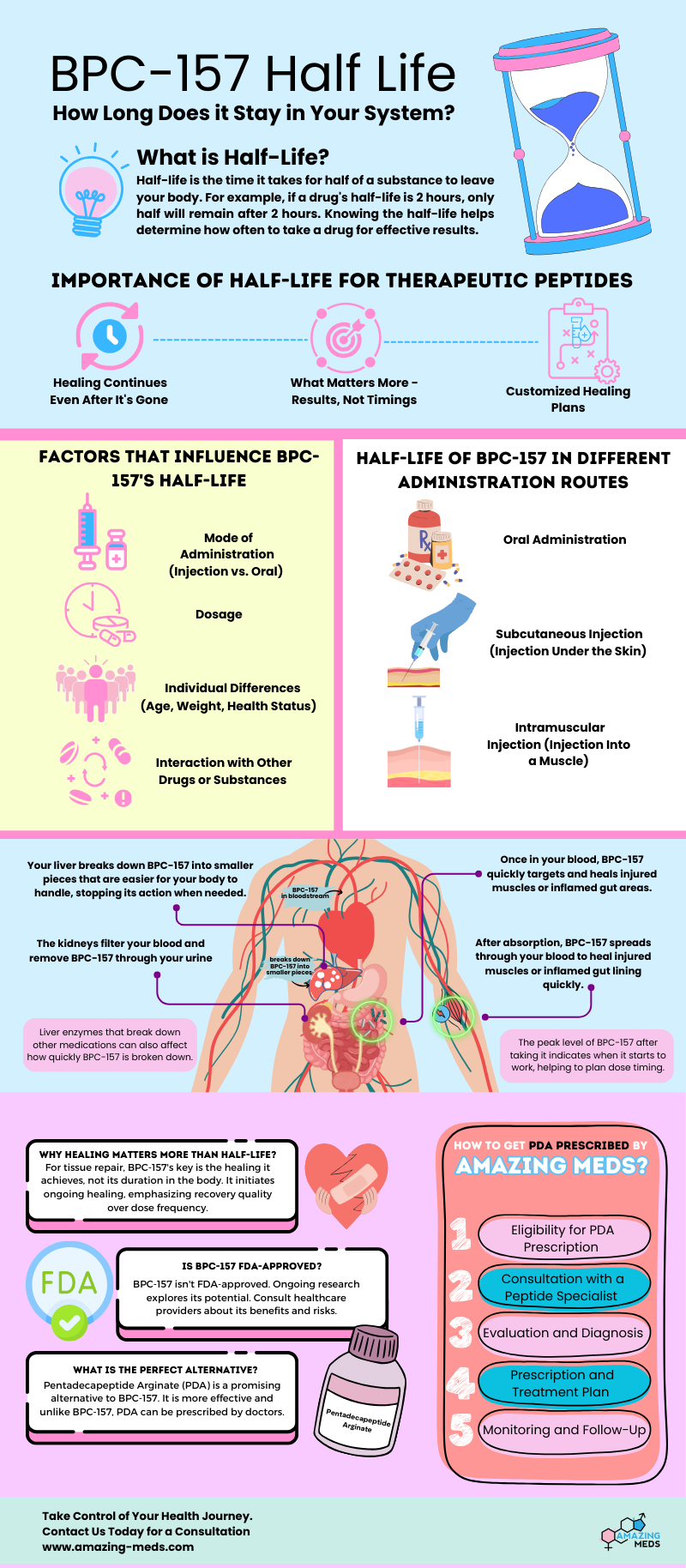
Understanding BPC-157’s Half-Life
The half-life of a substance refers to the time it takes for its concentration in the body to reduce by half. This is a critical factor in determining how frequently and at what dosage a substance should be administered to maintain a therapeutic effect.
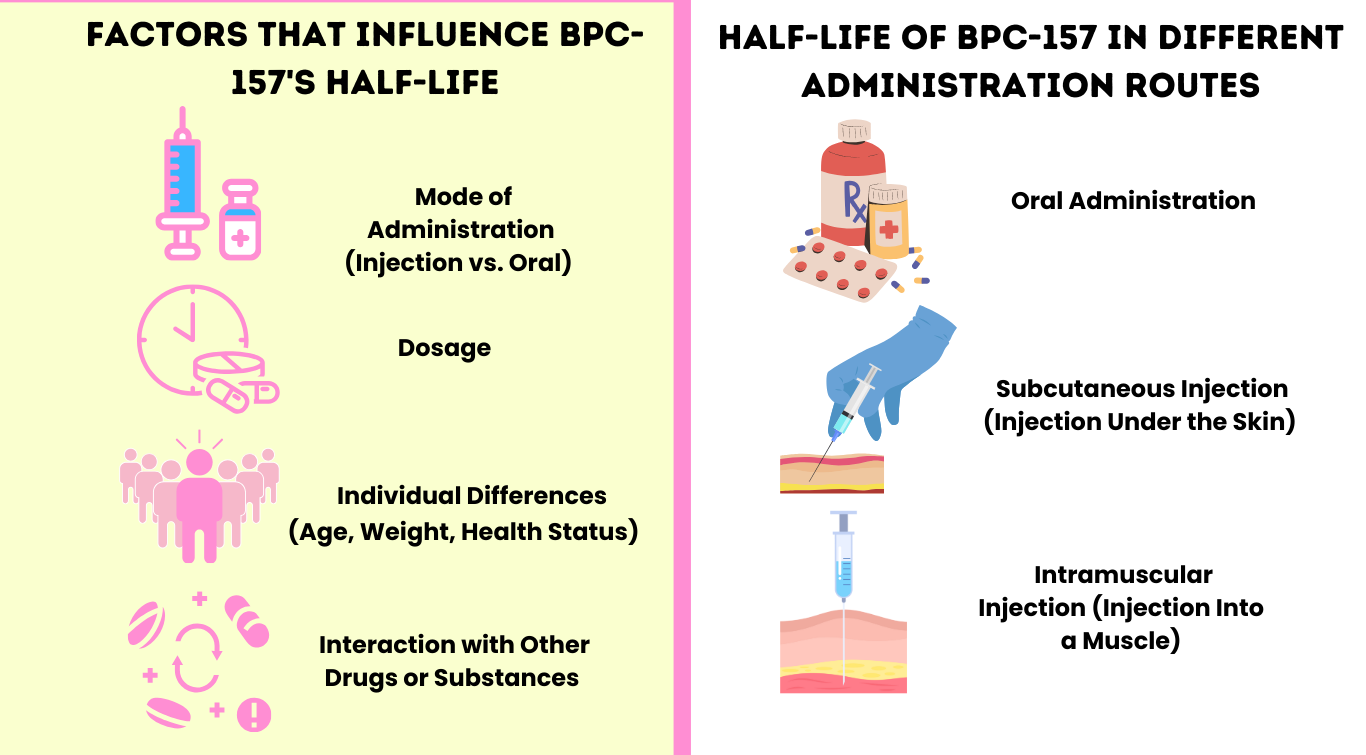
- Oral Administration: When taken orally, BPC-157 has a relatively short half-life, estimated to be around 2-4 hours. This means that after 2-4 hours, half of the BPC-157 in your system will be metabolized.
- Subcutaneous Injection: Subcutaneous (under the skin) injection is a common method of administration. The half-life via this route is also estimated to be relatively short, potentially similar to oral administration, around 2-4 hours. The bioavailability is significantly higher with this method.
- Intramuscular Injection: Intramuscular (into the muscle) administration may offer a slightly longer half-life, potentially allowing for less frequent dosing compared to oral or subcutaneous routes. However, the exact half-life via intramuscular injection is still under investigation.
The short half-life of BPC-157 necessitates frequent administration to maintain consistent levels in the body.
Dosage Recommendations for BPC-157
Dosage recommendations for BPC-157 vary depending on the route of administration and the individual’s needs. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or peptide regimen. The following are general guidelines:
- Oral Dosage: Common oral dosages range from 250 mcg to 500 mcg, taken twice daily. Due to the lower bioavailability, higher doses may be necessary to achieve desired effects.
- Subcutaneous Injection Dosage: A typical starting dose is 250 mcg to 500 mcg, administered once or twice daily. This method offers higher bioavailability than oral administration.
- Intramuscular Injection Dosage: Dosage recommendations for intramuscular injection are similar to subcutaneous, generally ranging from 250 mcg to 500 mcg, administered once or twice daily.
Important Considerations for Dosage:
- Individual Factors: Body weight, metabolism, and overall health can influence the optimal dosage.
- Specific Goals: The desired therapeutic effect (e.g., tendon healing, gut health) may influence the dosage.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Start with a lower dose and gradually increase it as needed, while carefully monitoring your body’s response.
- Professional Guidance: Always prioritize consulting with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized dosage recommendations.
Administration Methods: Oral vs. Injection
The method of administration significantly impacts BPC-157’s effectiveness and bioavailability.
- Oral Administration:
- Pros: Convenient and non-invasive.
- Cons: Lower bioavailability, meaning a smaller percentage of the peptide is absorbed into the bloodstream. May require higher doses.
- Subcutaneous Injection:
- Pros: Higher bioavailability than oral administration, potentially leading to better results.
- Cons: Requires self-injection, which may be a deterrent for some.
- Intramuscular Injection:
- Pros: Highest bioavailability.
- Cons: Requires self-injection into muscle, which may be more painful.
The best method depends on individual preferences, goals, and the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Considerations
While generally considered safe, BPC-157 can potentially cause side effects.
- Common Side Effects: Minor side effects, such as mild headaches, nausea, or injection site reactions (redness, swelling), may occur.
- Long-Term Safety: The long-term effects of BPC-157 are not fully understood.
- Contraindications: It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider of all medications, supplements, and pre-existing medical conditions before starting BPC-157.
- Quality and Purity: Only purchase BPC-157 from reputable sources to ensure product quality and minimize the risk of contamination.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions about BPC-157
BPC-157 holds promise for its potential healing and regenerative properties. Understanding its half-life and appropriate dosage is essential for optimizing its use. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of BPC-157 administration. Remember to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or peptide regimen to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your individual needs. Always prioritize your health and well-being by making informed decisions based on professional guidance and reliable information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long should I cycle BPC-157?
The duration of a BPC-157 cycle varies depending on your goals and the guidance of your healthcare provider. Cycles typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, followed by a break. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate cycle length for you.
2. Is BPC-157 legal?
The legality of BPC-157 varies depending on the country and region. In many places, it is not a controlled substance but may be regulated as a research chemical or supplement. Always check the regulations in your area.
3. Can I stack BPC-157 with other peptides or supplements?
Yes, BPC-157 is often stacked with other peptides or supplements to enhance its effects. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the compatibility of different substances and to ensure safety.
4. Can BPC-157 be used for athletic performance enhancement?
While BPC-157 may aid in recovery, it is not currently approved for athletic performance enhancement. Athletes should be aware of any regulatory restrictions on the use of BPC-157 in their sport.
5. How do I store BPC-157?
Reconstituted BPC-157 should be stored in a refrigerator, generally between 2-8 degrees Celsius (35-46 degrees Fahrenheit). Unreconstituted (lyophilized) BPC-157 should be stored at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific storage recommendations.