The Application Roadmap Template That Works: A Guide to Strategic Software Development
In the fast-paced world of software development, clarity and direction are paramount. A well-defined application roadmap acts as your compass, guiding your team from the initial concept to the final product and beyond. But building a roadmap that truly works requires more than just a pretty picture; it needs a structured approach that aligns with your business goals and adapts to evolving market demands. This article will delve into the essential elements of a successful application roadmap template, helping you plan, execute, and deliver exceptional software.
What is an Application Roadmap and Why Do You Need One?
An application roadmap is a strategic, high-level plan that outlines the evolution of a software application over a specific period. It serves as a central point of reference for all stakeholders, including:
- Product Managers: Define the vision and strategy.
- Development Teams: Understand priorities and timelines.
- Stakeholders (Executives, Investors): Track progress and understand the future direction.
- Marketing and Sales: Align messaging and prepare for product launches.
The benefits of a robust application roadmap are numerous, including:
- Increased Alignment: Ensures everyone is on the same page regarding goals and priorities.
- Improved Prioritization: Helps make informed decisions about feature development and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Communication: Provides a clear and concise way to communicate plans and progress.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Allows for early identification of potential challenges and risks.
- Greater Agility: Enables teams to adapt to market changes and customer feedback.
Key Elements of a Successful Application Roadmap Template
While the specific format of your roadmap may vary, certain core elements are crucial for its effectiveness.
1. Vision and Goals
- Define the overarching vision for the application. What problem are you solving? What impact do you aim to make?
- Establish clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These serve as the foundation for all roadmap decisions.
- Outline key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress towards your goals. Examples include user acquisition, retention, and revenue.
2. Themes and Initiatives
- Group features and functionalities into thematic areas. This helps organize the roadmap and provides a high-level view of development priorities. Examples include:
- Performance & Scalability: Optimizing the app’s speed and handling user load.
- User Experience (UX) Improvements: Enhancing usability and user satisfaction.
- New Feature Development: Introducing new functionalities to meet user needs.
- Security & Compliance: Ensuring data protection and adhering to regulations.
- Identify key initiatives within each theme. These are the specific projects or tasks that will drive progress.
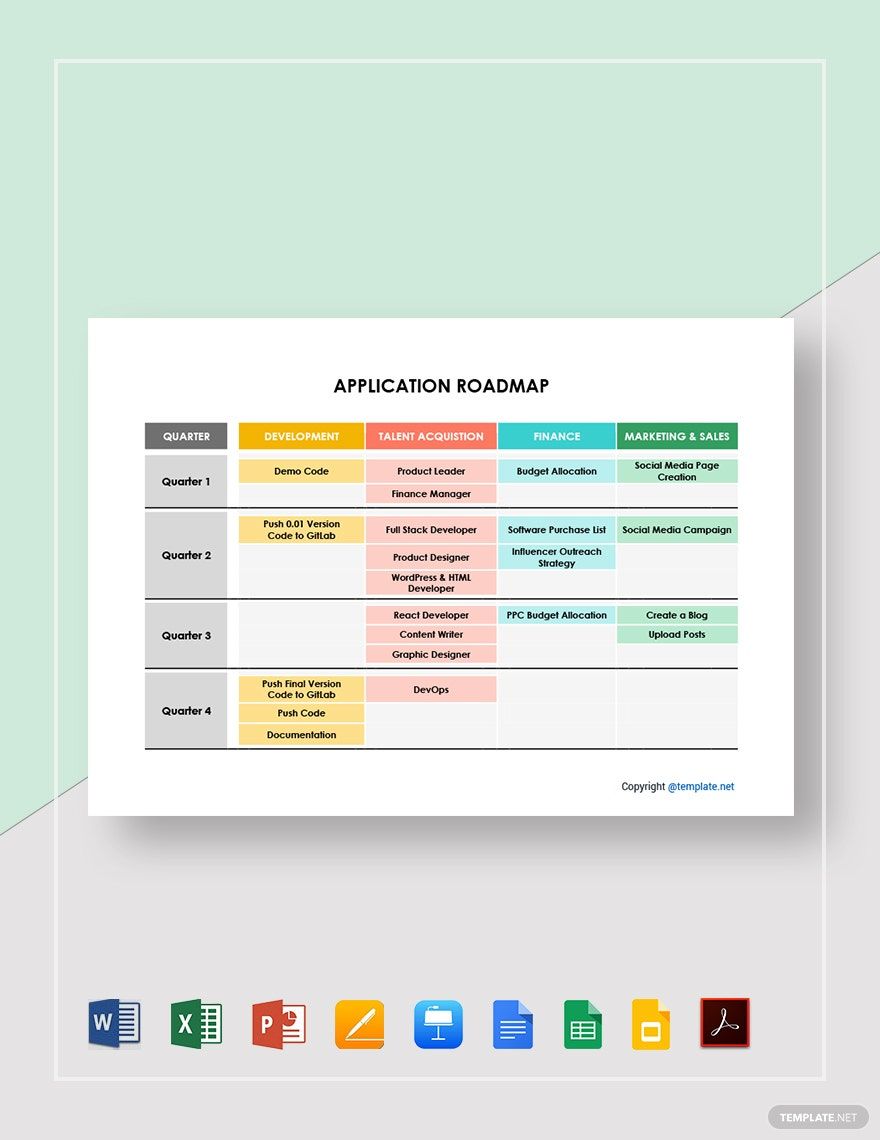
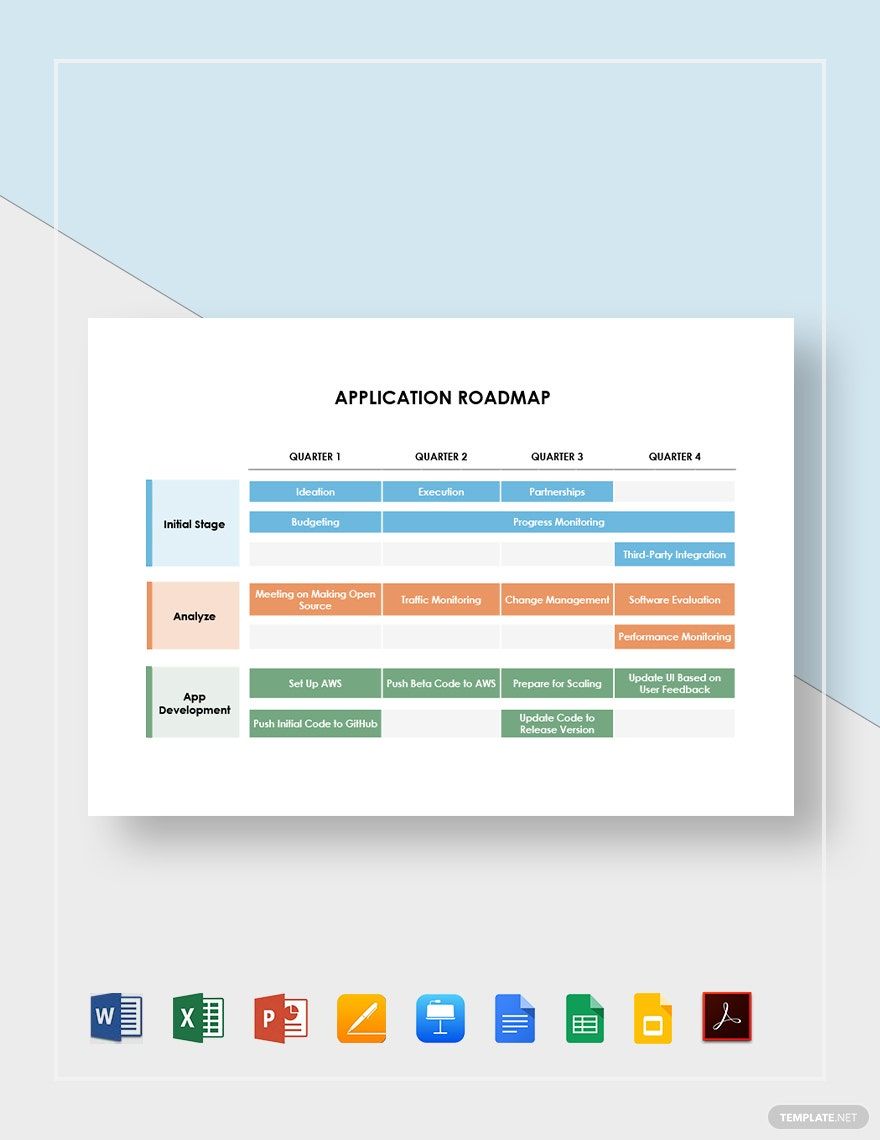
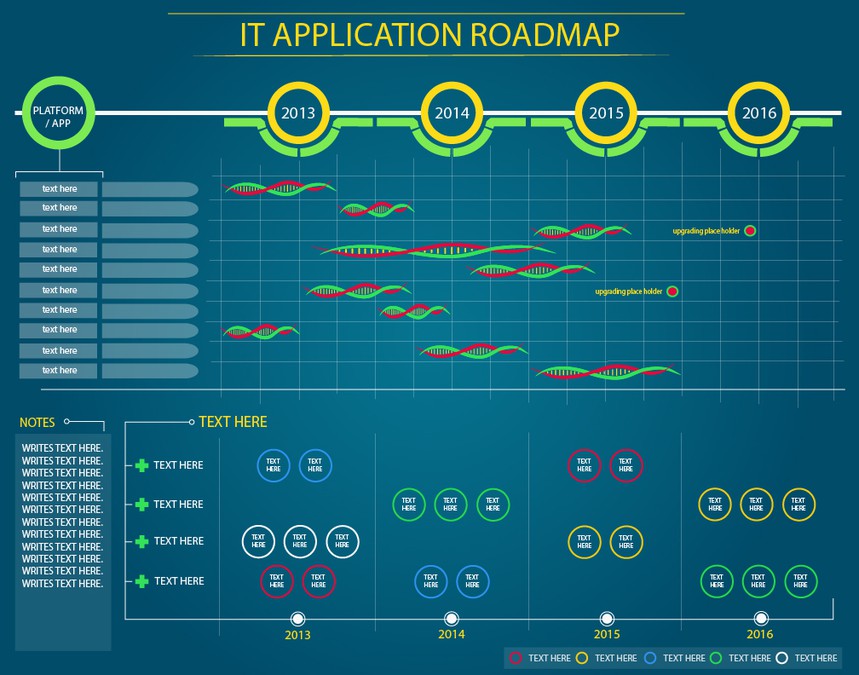
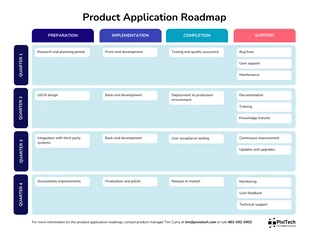
3. Timeline and Release Planning
- Establish a clear timeline for development, including quarters, milestones, and release dates. Be realistic and consider potential delays.
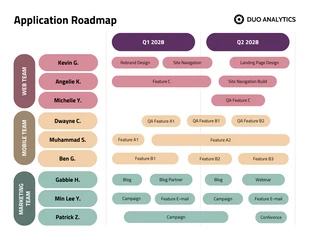
- Use a visual timeline format, such as a Gantt chart or a Kanban board, to represent the roadmap. This makes it easier to understand the schedule at a glance.
- Consider different release cadences, such as Agile sprints or quarterly releases. Choose the approach that best suits your development process.
4. Prioritization and Feature Breakdown
- Prioritize features based on their impact on your goals, market demand, and available resources. Use frameworks like the MoSCoW method (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) or the RICE scoring model (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort).
- Break down features into smaller, manageable tasks or user stories. This facilitates development and allows for iterative progress.
- Assign owners or responsible parties for each feature or task.
5. Technology and Architecture
- Document the core technologies and architecture used in the application. This provides context and helps guide technical decisions.
- Outline any planned technology updates, migrations, or integrations.
- Consider the scalability and maintainability of the application.
6. Communication and Collaboration
- Establish a regular schedule for roadmap reviews and updates.
- Share the roadmap with all stakeholders and encourage feedback.
- Use a collaboration platform, such as a project management tool or a shared document, to facilitate communication and ensure everyone has access to the latest information.
Tools and Templates for Building Your Roadmap
Several tools and templates can help you create and manage your application roadmap:
- Project Management Software: Jira, Asana, Monday.com, Trello (for basic roadmaps).
- Specialized Roadmap Tools: Productboard, Aha!, Roadmunk.
- Spreadsheet Templates: Google Sheets, Microsoft Excel (for simpler roadmaps).
- Presentation Software: PowerPoint, Google Slides (for visual communication).
Choose the tool that best aligns with your team’s size, budget, and complexity of the application.
Iteration and Adaptation: The Key to Long-Term Success
An application roadmap is not a static document. It should be a living, breathing entity that evolves as your product and the market change.
- Regularly review and update your roadmap based on feedback, market trends, and performance data.
- Be prepared to adjust your priorities and timelines as needed.
- Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Conclusion: Building a Roadmap that Drives Success
Creating a successful application roadmap is a critical step in ensuring your software project achieves its goals. By following the framework outlined above, incorporating key elements, and embracing a culture of iteration, you can create a roadmap that guides your team to success. Remember to tailor your roadmap to your specific needs and continuously refine it based on feedback and market changes. With a well-defined roadmap, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of software development and deliver a product that delights your users.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should I update my application roadmap?
The frequency of updates depends on your development methodology and the pace of change in your market. A good starting point is to review and update your roadmap at least quarterly. However, you may need to adjust more frequently if you are using Agile methodologies or if your market is rapidly evolving.
2. What is the difference between a product roadmap and an application roadmap?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, a product roadmap is usually a broader strategic plan encompassing all aspects of a product, including marketing, sales, and support. An application roadmap, on the other hand, focuses specifically on the development and evolution of the software application itself.
3. How can I get buy-in from stakeholders on my application roadmap?
Involve stakeholders in the roadmap creation process from the beginning. Clearly communicate the benefits of the roadmap, such as improved alignment and transparency. Regularly share the roadmap with stakeholders, solicit their feedback, and address their concerns.
4. Should I include technical details in my application roadmap?
The level of technical detail depends on your audience. For a high-level roadmap aimed at executives, focus on themes and initiatives. For development teams, include more technical details, such as technologies, architecture, and feature breakdowns.
5. What if my roadmap is too ambitious?
Be realistic when setting goals and estimating timelines. If your roadmap is overly ambitious, prioritize features and be prepared to adjust your plans. Consider using a phased approach, releasing new features in increments, and gathering user feedback along the way.