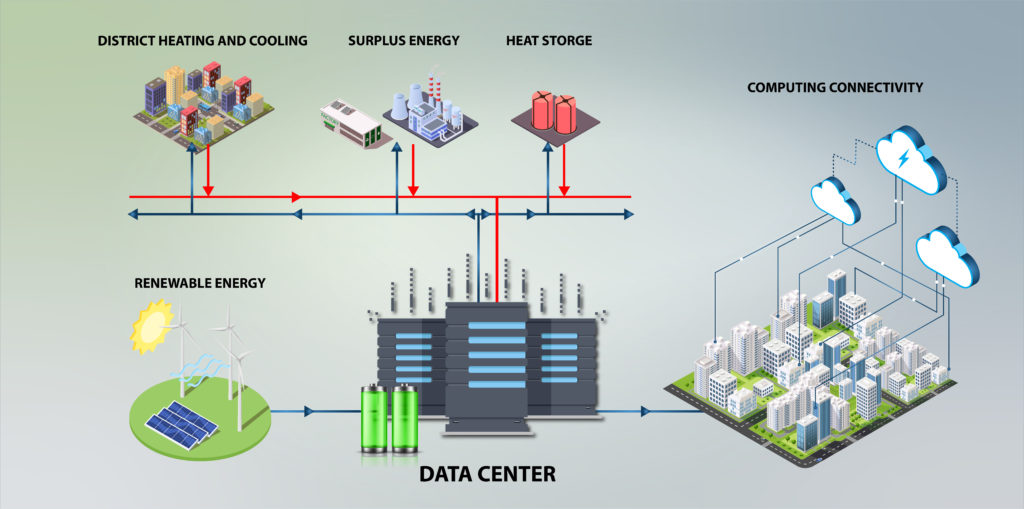
Metas San Jose PPG&F Data Center: Examining Environmental Impact Concerns
The digital world thrives on data, and data centers are the engines that power it. As demand for cloud services, streaming, and online applications explodes, so too does the growth of these massive facilities. The Metas San Jose PPG&F data center, like others of its kind, faces increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental footprint. This article delves into the specific environmental impact concerns surrounding this data center, providing a balanced and informative overview. We’ll explore the challenges, potential solutions, and the importance of sustainable practices in this rapidly evolving industry.
Understanding the Scope: The Metas San Jose PPG&F Data Center
Before we delve into the environmental impacts, it’s important to understand what the Metas San Jose PPG&F data center represents. While specific details about this facility are often proprietary, we can extrapolate based on industry standards and common practices. Data centers like this are typically:
- Massive facilities: Housing thousands of servers, networking equipment, and storage devices.
- Power-hungry: Requiring significant amounts of electricity to operate and cool equipment.
- Water-intensive: Employing water for cooling purposes in many cases.
- Located in strategic areas: Often chosen for their proximity to power grids, fiber optic networks, and available land.
Key Environmental Impact Concerns
The primary environmental concerns associated with data centers like the Metas San Jose PPG&F facility revolve around several key areas:
- Energy Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions: This is arguably the most significant concern. Data centers consume vast amounts of electricity, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions depending on the energy source used (e.g., fossil fuels vs. renewable energy).
- Impact: Increased carbon footprint, contributing to climate change.
- Considerations: The source of electricity, the efficiency of the facility’s power usage effectiveness (PUE), and the overall energy demand.
- Water Usage: Cooling servers generates significant water consumption, especially in areas with limited water resources.
- Impact: Water scarcity, strain on local water supplies.
- Considerations: Cooling methods employed (e.g., air cooling vs. water cooling), water source, and water recycling strategies.
- Electronic Waste (e-waste): The rapid obsolescence of IT equipment leads to a significant volume of electronic waste.
- Impact: Pollution from hazardous materials, landfill burden.
- Considerations: Proper e-waste management, recycling programs, and the lifespan of equipment.
- Land Use: Data centers require substantial land areas, potentially impacting local ecosystems and land use patterns.
- Impact: Habitat loss, potential for environmental degradation.
- Considerations: Site selection, landscaping practices, and the overall footprint of the facility.
Mitigation Strategies and Sustainable Practices
Fortunately, the data center industry is increasingly aware of its environmental impact and actively exploring and implementing strategies for mitigation:
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Sourcing electricity from renewable sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power.
- Improving Energy Efficiency: Implementing advanced cooling systems, optimizing server utilization, and improving Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) scores.
- Water Conservation: Utilizing water-efficient cooling technologies (e.g., air cooling, adiabatic cooling), implementing water recycling programs, and sourcing water from sustainable sources.
- E-waste Management: Implementing robust e-waste recycling programs, extending the lifespan of equipment, and promoting circular economy principles.
- Sustainable Site Selection: Choosing locations with access to renewable energy, existing infrastructure, and minimal environmental impact.
- Data Center Design: Implementing sustainable designs to minimize the environmental impact, such as using sustainable building materials and implementing green roofs.
The Role of Transparency and Accountability
Increased transparency and accountability are crucial for fostering sustainable practices within the data center industry. This includes:
- Public Reporting: Data centers should publicly report their energy consumption, water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Certifications and Standards: Adhering to industry standards and certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and others that validate sustainability efforts.
- Collaboration: Working with governments, communities, and industry partners to develop and implement sustainable solutions.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Digital Future
The Metas San Jose PPG&F data center, like other data centers globally, faces significant environmental challenges. However, the industry is actively working to address these concerns through technological innovation, sustainable practices, and increased transparency. By embracing renewable energy, improving efficiency, conserving resources, and prioritizing responsible waste management, data centers can play a vital role in building a more sustainable digital future. The ongoing commitment to these principles is essential to ensuring the continued growth of the digital economy while minimizing its environmental footprint.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the environmental impact of data centers:
What is PUE, and why is it important? PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) measures a data center’s energy efficiency. It’s calculated by dividing the total power used by the facility by the power used by the IT equipment. A lower PUE indicates greater efficiency, meaning less energy is wasted on cooling and other support systems.
How do data centers contribute to water scarcity? Water is often used for cooling servers. In areas with limited water resources, this can strain local water supplies and contribute to water scarcity. Data centers are increasingly adopting water-efficient cooling technologies to address this.
What is being done about e-waste from data centers? Data centers are implementing e-waste recycling programs to properly dispose of old equipment and prevent hazardous materials from entering landfills. They are also exploring ways to extend the lifespan of equipment through refurbishment and reuse.
Are all data centers equally bad for the environment? No. The environmental impact of a data center depends on various factors, including its location, energy source, cooling methods, and waste management practices. Data centers that prioritize sustainability have a significantly lower environmental impact.
How can I support sustainable data center practices? You can support sustainable data center practices by choosing cloud providers and services that prioritize sustainability and transparency, advocating for renewable energy policies, and educating yourself and others about the importance of environmental responsibility in the digital age.