Birth Control Pill Failure: Could Probiotics Be to Blame? Exploring the Connection
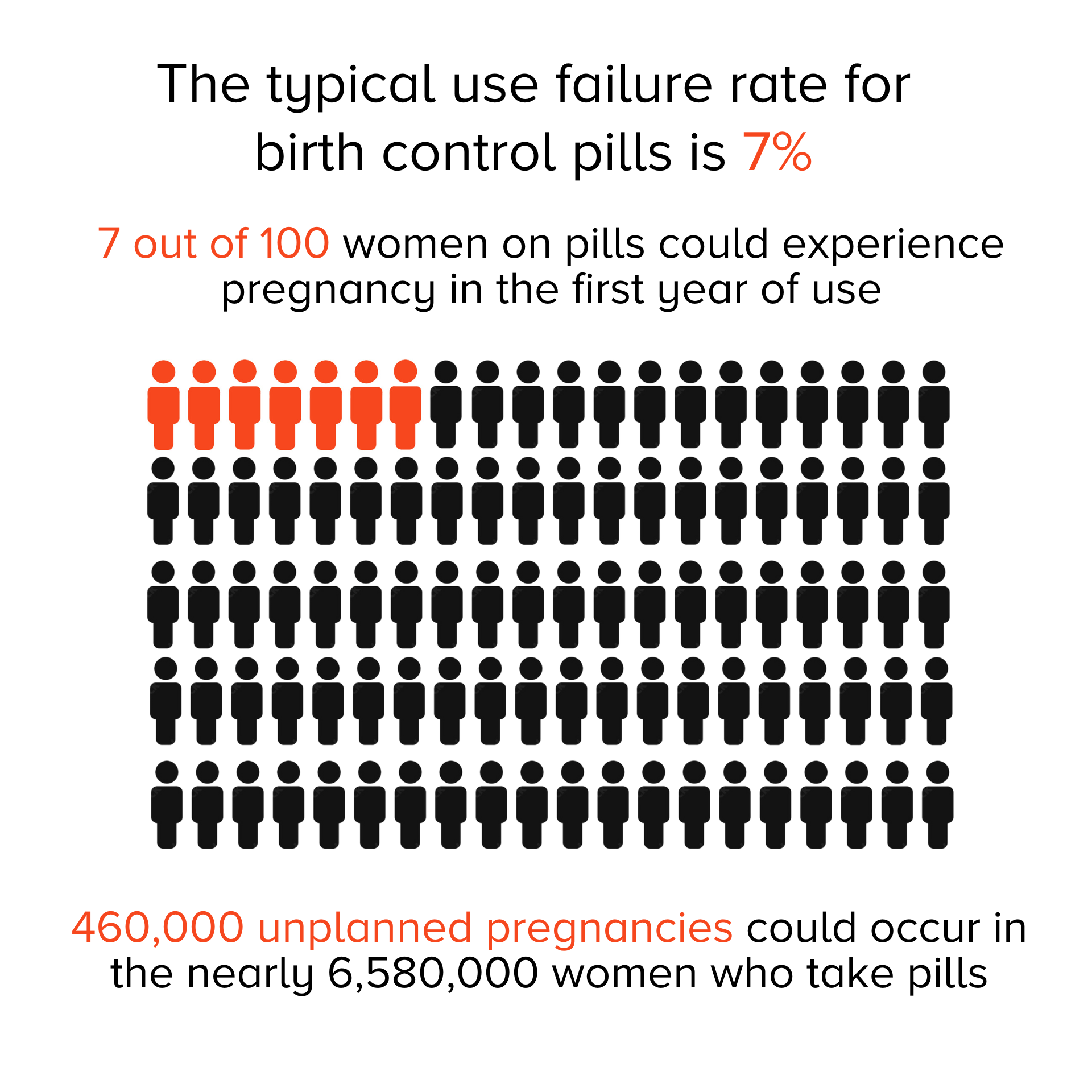
The birth control pill is a highly effective method of preventing pregnancy when taken correctly. However, like any medication, it’s not foolproof. While user error is often a primary suspect when a birth control pill fails, recent research and growing awareness are exploring a potentially unexpected culprit: probiotics. This article delves into the complex relationship between probiotics, the gut microbiome, and the effectiveness of birth control pills, providing a comprehensive understanding of the potential implications.
The Birth Control Pill: How Does it Work?
Before exploring the potential interference of probiotics, it’s crucial to understand how birth control pills function. Most combination pills (containing estrogen and progestin) work by:
- Preventing ovulation: Stopping the release of an egg from the ovaries.
- Thickening cervical mucus: Making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
- Thinning the uterine lining: Making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant.
The effectiveness of these mechanisms depends on consistent hormone levels, which can be impacted by various factors.
The Gut Microbiome: Your Body’s Inner Ecosystem
The gut microbiome is the complex community of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms that reside in your digestive tract. This ecosystem plays a vital role in:
- Digestion and nutrient absorption: Breaking down food and extracting essential nutrients.
- Immune system function: Protecting against harmful pathogens.
- Hormone regulation: Influencing the production and metabolism of hormones, including estrogen.
This last point is where the potential connection to birth control pill failure arises.
Probiotics: Boosting Gut Health and Potential Interactions
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often bacteria, that, when consumed, provide health benefits. They are commonly found in:
- Yogurt and fermented foods: Such as kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha.
- Dietary supplements: Available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders.
While generally considered safe, probiotics can sometimes have unintended consequences, particularly concerning their interaction with other medications.
How Could Probiotics Affect Birth Control Pill Effectiveness?
The primary concern lies in the potential impact of probiotics on estrogen levels and the liver’s ability to process the birth control pill. Here’s a breakdown:
- Estrogen Metabolism: The gut microbiome plays a role in the enterohepatic circulation of estrogen. Some gut bacteria produce an enzyme called beta-glucuronidase. This enzyme can reactivate estrogen that has already been metabolized by the liver, leading to a rebound in estrogen levels.
- Liver Function and Drug Metabolism: The liver is responsible for metabolizing both estrogen and the synthetic hormones in birth control pills. If probiotics significantly alter liver function, it could potentially speed up or slow down the metabolism of the pill, affecting its effectiveness.
- Drug Absorption: While less researched, it’s theoretically possible that certain probiotics or changes in the gut environment could affect the absorption of the birth control pill from the digestive tract.
Important Note: The research in this area is still evolving, and definitive evidence linking probiotic use to birth control pill failure is limited. However, the potential for interaction warrants consideration.
What the Research Says (and Doesn’t Say)
- Limited Direct Studies: There is not a large body of direct research specifically examining the interaction between probiotics and birth control pill efficacy.
- Focus on Other Medications: Some studies have explored the impact of probiotics on the effectiveness of other medications metabolized by the liver, providing a theoretical framework for potential interactions.
- Individual Variability: The impact of probiotics can vary significantly depending on the specific probiotic strain, the individual’s gut microbiome composition, and other factors.
Should You Be Concerned? Steps to Take
If you are taking birth control pills and also taking probiotics, consider the following:
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They can assess your individual risk factors and provide personalized advice.
- Be Aware of Side Effects: Monitor for any changes in bleeding patterns, breakthrough bleeding, or other potential signs of reduced birth control effectiveness.
- Consider Timing: If your doctor advises, you could consider spacing out the doses of your birth control pill and probiotic. However, this should be done under medical guidance.
- Use Backup Contraception: If you experience any concerns about the effectiveness of your birth control, use a backup method, such as condoms, until you can consult with your doctor.
Conclusion: Navigating the Intersection of Probiotics and Birth Control
While the exact relationship between probiotics and birth control pill effectiveness remains under investigation, the potential for interaction exists. As more research emerges, a clearer picture will develop. In the meantime, open communication with your healthcare provider and proactive monitoring of your body are essential for ensuring the reliability of your chosen contraception. The key takeaway is to be informed, proactive, and prioritize your reproductive health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can probiotics make my birth control pills ineffective?
The evidence is limited, and there is not a definitive answer. However, there is theoretical potential for interaction. It is crucial to discuss any concerns with your doctor.
2. Should I stop taking probiotics if I’m on birth control?
It’s best to consult with your doctor. They can assess your individual situation and advise on the best course of action. They might recommend adjustments to timing or the use of backup contraception.
3. Are all probiotic strains equally likely to interfere with birth control?
The impact of different probiotic strains can vary. Research is still ongoing to identify specific strains that may pose a greater risk.
4. Can I take probiotics and birth control pills at the same time?
This depends on your individual circumstances and your doctor’s recommendations. If advised, you may need to space out the doses or use a backup method.
5. What are the signs that my birth control might not be working?
Possible signs include breakthrough bleeding, spotting between periods, changes in your menstrual cycle, and, of course, a positive pregnancy test. If you experience these, consult your doctor immediately.