2000 Ford F250 Super Duty Fuse Box: The Map Owners Wish They Had Sooner
Owning a 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty is a testament to your appreciation for a powerful and reliable workhorse. But even the toughest trucks need a little TLC, and electrical issues are a common source of frustration. When a light flickers, a power window fails, or the radio goes silent, the fuse box is often the first place to investigate. This guide provides a comprehensive look at the 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty fuse box, helping you troubleshoot electrical problems efficiently and avoid unnecessary trips to the mechanic. Think of it as the map you wish you had when you first bought your truck!
Understanding Your 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty Fuse Boxes
The 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty has two primary fuse boxes:
- The Interior Fuse Box (Passenger Compartment): Located inside the cab, usually on the driver’s side, this box protects circuits for interior lights, power windows, the radio, the instrument cluster, and other in-cabin functions.
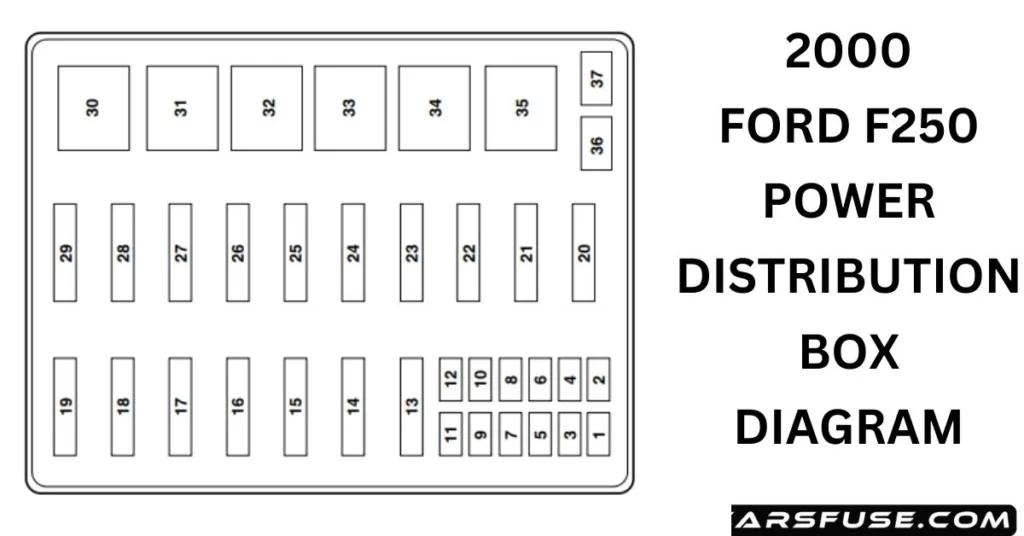
- The Power Distribution Box (Under the Hood): This box, located under the hood near the battery, safeguards circuits for the engine, headlights, horn, air conditioning, anti-lock brakes, and other essential components.
Knowing the location of both fuse boxes is the first step in diagnosing electrical issues.
Locating Your Fuse Boxes
- Interior Fuse Box: Locate the driver’s side dashboard. You might need to remove a small panel or access it behind a trim piece. Consult your owner’s manual for the exact location and access procedure for your specific model, as variations exist.
- Power Distribution Box: This is typically a black plastic box located near the battery in the engine compartment. It should be clearly labeled.
Decoding the Fuse Box Layout: A Detailed Guide
Each fuse box contains a diagram, often printed on the inside of the cover, which identifies each fuse and its corresponding circuit. However, these diagrams can sometimes be difficult to decipher or even missing. Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know:
- Fuse Amperage: Fuses are rated by amperage (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A, 30A). This number indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before it blows, protecting the circuit from damage.
- Fuse Types: Your 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty likely uses blade-type fuses. Familiarize yourself with the different colors and sizes, as they denote the amperage rating.
- Circuit Protection: Each fuse protects a specific electrical circuit. The diagram will indicate which circuit each fuse controls (e.g., “Radio,” “Headlights,” “Power Windows”).
- Relays: You might also find relays in the power distribution box. Relays are electromagnetic switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal.
To effectively diagnose a problem:
- Consult the Diagram: Always start by consulting the fuse box diagram.
- Identify the Affected Circuit: Determine which circuit is experiencing the problem (e.g., the headlights aren’t working).
- Locate the Corresponding Fuse: Find the fuse that protects that circuit.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken filament. Use a fuse puller (often included in the fuse box) to safely remove the fuse.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the exact same amperage and type. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can damage the circuit.
Common Electrical Issues and Their Corresponding Fuses
Here are some common electrical problems and the fuses you might need to check:
- Headlights Not Working: Check the fuse labeled “Headlights” or “Low Beam” and “High Beam” in the Power Distribution Box. Also, check the associated relay.
- Radio Not Working: Check the fuse labeled “Radio” or “Audio” in the Interior Fuse Box.
- Power Windows Not Working: Check the fuse labeled “Power Windows” in the Interior Fuse Box.
- Horn Not Working: Check the fuse labeled “Horn” in the Power Distribution Box.
- Brake Lights Not Working: Check the fuse labeled “Brake Lights” in the Interior Fuse Box, and inspect the brake light switch located near the brake pedal.
Important Safety Note: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on electrical components to prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
Troubleshooting Tips and Best Practices
- Carry Spare Fuses: Keep a set of spare fuses of various amperages in your truck. This will save you time and frustration when a fuse blows.
- Use a Fuse Puller: A fuse puller is a small plastic tool designed to remove fuses safely and easily.
- Consider a Multimeter: A multimeter can be used to test fuses for continuity and diagnose more complex electrical problems.
- Check for Loose Connections: Sometimes, a loose wire or connector can cause electrical issues. Inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors in the affected circuit.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re uncomfortable working with electrical systems or the problem persists after replacing fuses, consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
Understanding the fuse box in your 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty is crucial for maintaining your truck and addressing electrical problems quickly and efficiently. By familiarizing yourself with the fuse box layout, knowing how to identify and replace blown fuses, and following the troubleshooting tips provided, you can often resolve electrical issues yourself, saving time and money. This guide provides the foundational knowledge to navigate your truck’s electrical system with confidence. Now you have the map!
FAQs
1. Where is the fuse box located in a 2000 Ford F250 Super Duty?
There are two fuse boxes: one inside the cab on the driver’s side (interior) and one under the hood near the battery (power distribution).
2. What do I do if a fuse keeps blowing?
If a fuse keeps blowing, there’s an underlying electrical problem, such as a short circuit or an overloaded circuit. Do not use a higher amperage fuse. You’ll need to inspect the wiring and components in the affected circuit for damage or shorts. Consult a professional if you’re unsure.
3. Can I use a fuse with a higher amperage rating?
No. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified can damage the circuit and potentially cause a fire. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the exact same amperage.
4. What is the purpose of a relay?
A relay is an electromagnetic switch that allows a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They are often used to control high-power components like headlights, horns, and starter motors.
5. How do I find the correct fuse for a specific component?
Consult the fuse box diagram, often located on the inside of the fuse box cover. The diagram identifies which fuse controls each circuit. If the diagram is missing or unclear, consult your owner’s manual or a reputable online resource for the correct fuse locations.